Starlink’s Direct-to-Cell service is a new technology that allows Starlink satellites to provide cellular connectivity directly to mobile devices. This service is designed to provide ubiquitous access to texting, calling, and browsing wherever you may be, including remote regions and areas with traditionally poor cellular coverage.

The Direct-to-Cell service works with existing LTE phones and does not require any changes to hardware, firmware, or special apps. The Starlink satellites equipped with this capability have an advanced eNodeB modem onboard that acts like a cellphone tower in space, allowing network integration similar to a standard roaming partner.
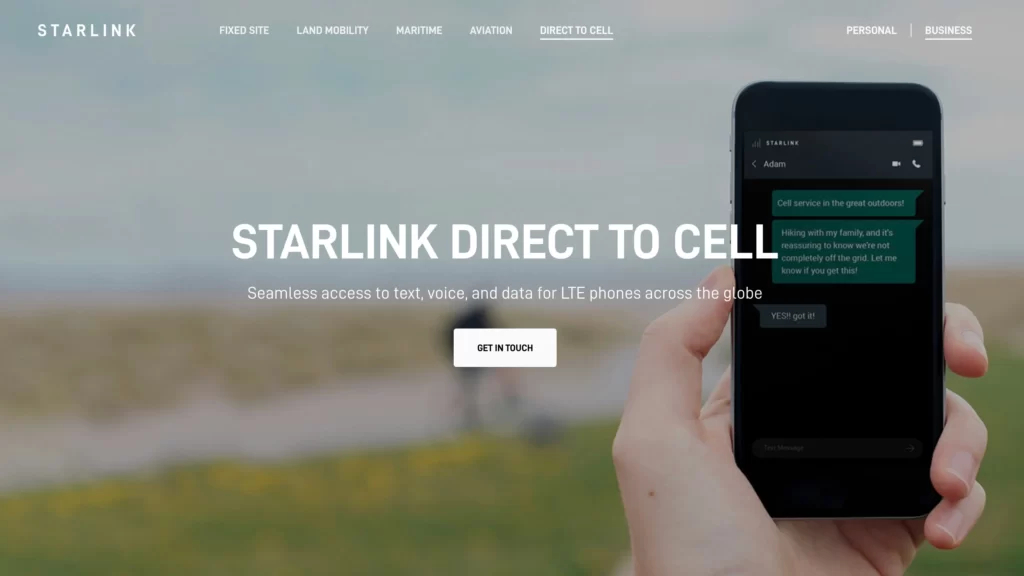
The service was launched in partnership with T-Mobile and other global partners, and it is expected to provide coverage in cellular dead zones . The first six Starlink satellites with Direct-to-Cell capabilities were launched in early January 2024. Initially, the service will enable text messaging, with voice and data coverage to follow as more satellites are launched.
The Direct-to-Cell service will also connect Internet of Things (IoT) devices, expanding the range of devices that can benefit from this technology.
However, it’s important to note that while this service can provide connectivity in areas with no cellular coverage, it is not intended to compete with existing terrestrial cellular networks. The service’s primary benefit is its wide coverage, rather than high-speed data transfer.
The service is currently being tested in the United States, with plans to expand globally in partnership with various cellular providers. Other companies, such as Amazon’s Project Kuiper and AST SpaceMobile, are also developing similar satellite direct-to-cell services.


