DeFi stands for Decentralized Finance.” Simply put, “DeFi” is a term given to various decentralized financial services that aim to replace our current centralized financial system.
DeFi takes components of traditional finance and decentralizes them by removing intermediaries and replacing them with smart contracts.
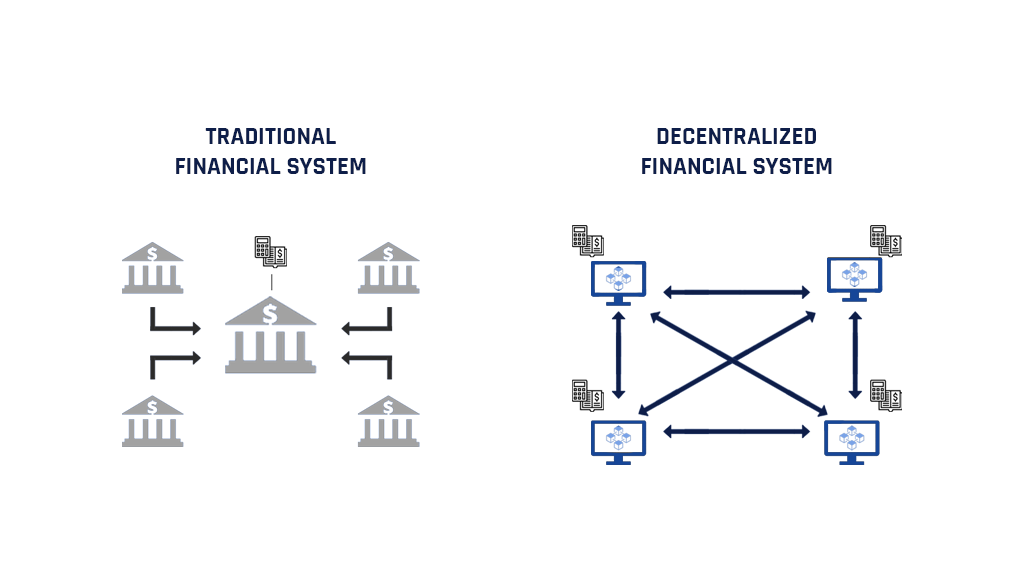
The goal of DeFi is to create a financial market that is open, trustless, and devoid of permission. DeFi technology focuses on improving the current economic system, resulting in a better user experience for those who use the technology (for both businesses and their clients).
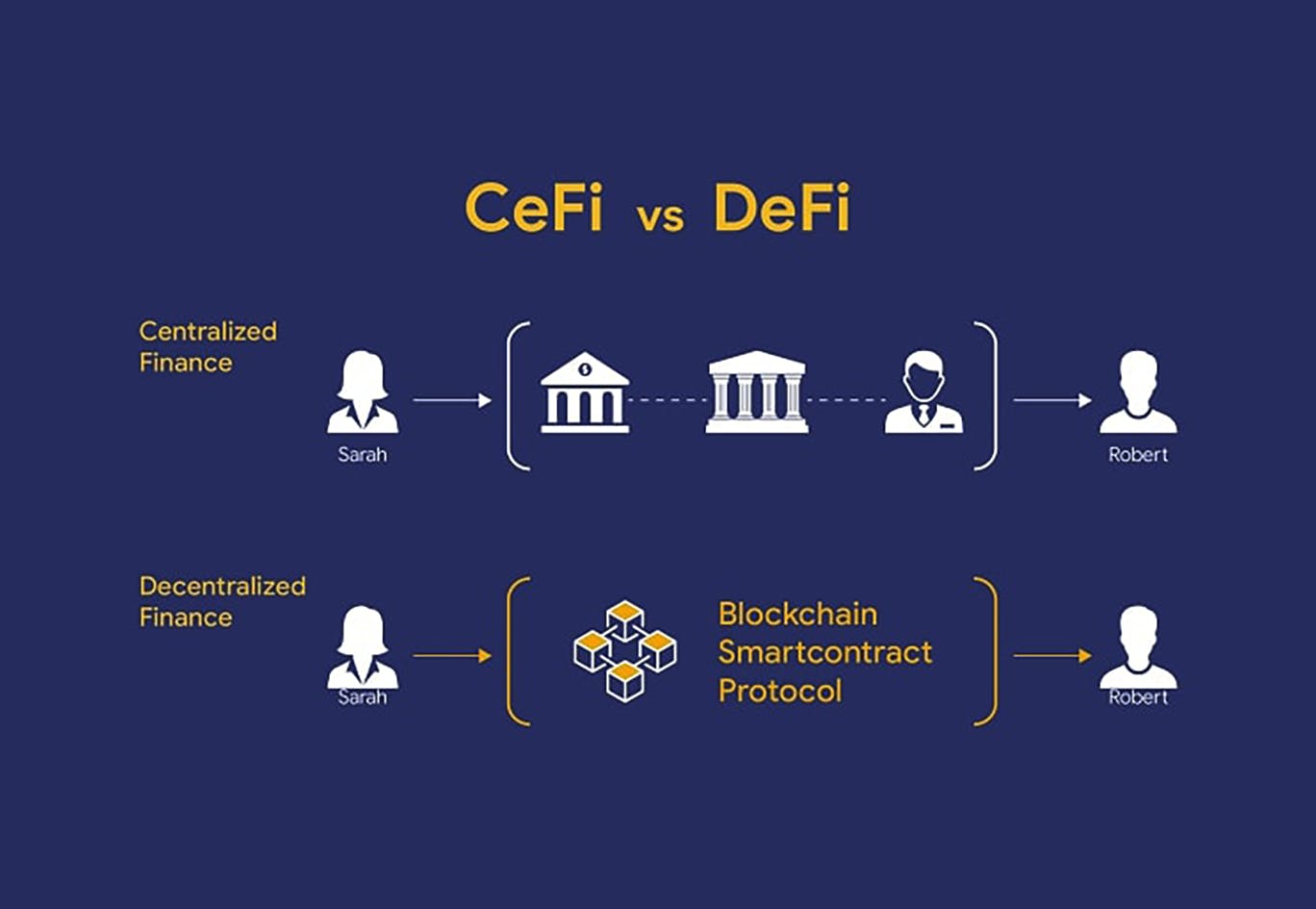
I’m not too fond of banks because their services are entirely centralized. There’s always someone in charge, and this comes with its own risks, like fraud and corruption. With centralized finance, a bank or corporation is holding your money. These guys don’t care about you, their sole purpose is to make money, and there are a lot of third parties, each charging a fee for using their services.
To fully understand DeFi, let’s look at Bitcoin, a payment system where anyone can send money to anyone worldwide. Bitcoin laid the foundation of the crypto revolution, and no bank or government controls it. I would love to call Bitcoin a form of decentralized money, not necessarily DeFi.

In a centralized financial system, there are many things you can do, from loaning, saving, insurance, and stock trading. The centralized financial system built its services around fiat currencies.
The idea behind decentralized finance is to decentralize the entire financial system, from lending, insurance, stock, and savings—similarly, Bitcoin decentralized money.
Now, using decentralized money like specific cryptocurrencies (stable coins) for automated activities, we can build exchanges like lending services, insurance companies, and other organizations that don’t have an owner, so no single entity controls them.
With DeFi, you can do most of the things that the centralized banks support, like earning interest, borrowing, lending, buying insurance, trading derivatives, trading assets, and even more.
The significant part is that, with DeFi, the process is much faster and doesn’t require paperwork or a third party.
To create a decentralized financial system, we need an infrastructure for programming and running decentralized services. Luckily for us, Ethereum does just that. Ethereum is a technology that’s home to digital money, global payments, and applications (Dapps).
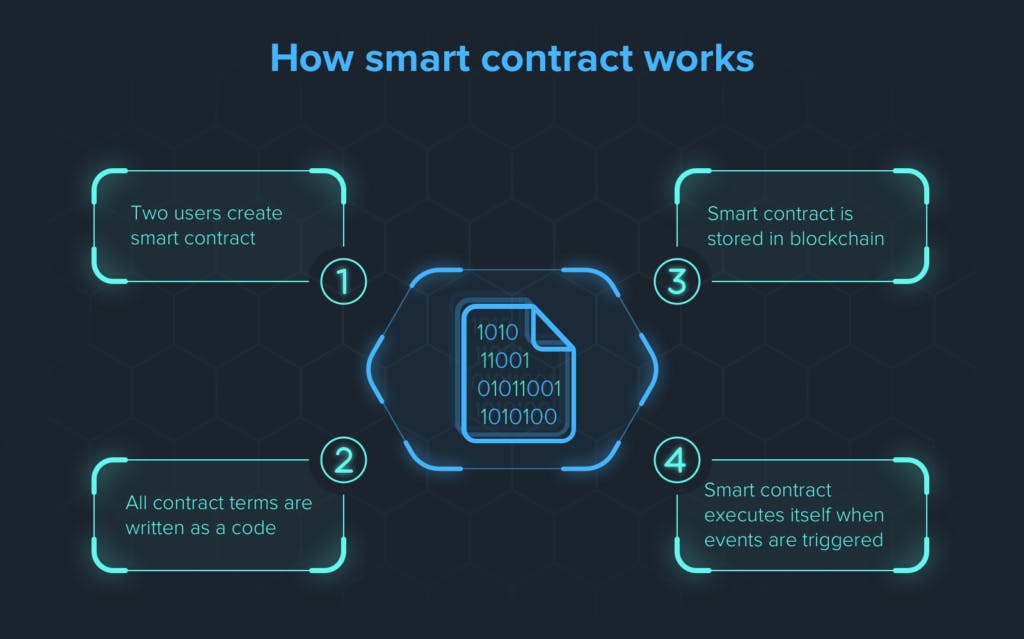
With Ethereum, we can write automated codes, also known as smart contracts. A smart contract is a self-executing program where you write the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller directly as code.
With smart contracts, we can manage any financial service we like to create in a decentralized manner. This means we can determine the rules for how a particular service should work, and once we deploy those rules on the Ethereum network, we no longer have control over them—they are immutable.
While Ethereum was the first smart contract blockchain, many others have risen to prominence, including Algorand, Solana, Binance Smart Chain, Cosmos, and others.
Once we have a system like Ethereum for creating decentralized apps (DApps), We can start building our decentralized financial system using a DApp, software running on a distributed network.
Not so fast, though! The first thing any financial system needs is money. I know what most likely comes to your mind is Bitcoin. Unfortunately, we can’t use that. The next best option is the Ether because it belongs to Ethereum. We can’t use that either.
Then Why Can’t We Use Bitcoin or Ether?
Bitcoin is decentralized, but it only has rudimentary programmable functionality, and it’s not compatible with the Ethereum platform. On the other hand, Ether is consistent and programmable; the problem is that it is highly volatile. We need a stable currency if we really want people to adopt these financial services.
Stable coins are cryptocurrencies pegged to the value of real-world assets, usually some primary currency like the U.S. dollar. For DeFi, we would want to stick to a stable coin that doesn’t use a fiat money reserve since it will require a central authority.
There are several stable coins out there – some of which are Ampleforth, Augment, DAI, DefiDollar, Digix, EOSDT, Empty Set Dollar, Frax, Gemini Dollar, HUSD, Money on Chain, Pax Dollar, pTokens, TrueUSD, USD Coin, WBTC

For this article, we will stick with DAI. DAI is a stable coin whose value is pegged to the U.S. dollar; this shields DAI from the wild swings in prices typically associated with cryptocurrencies. 1 DAI = 1$.

Fiat-collateralized stablecoins maintain a fiat currency reserve, like the U.S. dollar, as collateral to issue a suitable number of crypto coins. Tether (USDT) and TrueUSD (TUSD) are popular crypto coins with a value equivalent to a single U.S. dollar.
DAI is a form of crypto-collateralized stablecoin backed by other cryptocurrencies. Because the reserve cryptocurrency may also be prone to high volatility, these stablecoins are over-collateralized. A more significant number of crypto tokens are maintained as a reserve for issuing fewer stablecoins. This is publicly visible on the Ethereum blockchain.

Let me explain this. Let’s say you need to borrow 66 cents worth of DAI. You need to use $1 worth of Ether as collateral. As soon as you want your Ether back, pay back the DAI you borrowed, and the Ether will be released.
Loans within DeFi are more like getting a loan from a local pawnbroker. This works because customers can take an item like a car, a piece of jewelry, or anything of value and receive a loan based on the item’s value. The pawnbroker lends you 60% of the value of the item and charges you interest, and if you miss your repayment, they might sell your item to recoup the value of the loan. The pawnbroker will always lend you less than the value of the item you are putting up for collateral. This is known as an over-collateralized loan. Borrowing in DeFi is similar to this.

You can buy DAI on an exchange if you don’t have any ether to lock up as collateral because DAI is overcollateralized, even if Ether’s price becomes exceptionally volatile. The value of the locked Ether backing the DAI in circulation will most likely remain at 100% or more.
DAI stablecoin is also a smart contract on the Ethereum platform. Dai is a genuinely trustless decentralized stable coin that cannot be shut down or censored. Hence, it is a perfect form of money for other DeFi services.
Now that our decentralized financial system has stable decentralized money, It’s time to create some additional services.
DeFi Use Cases
Yield farming
They provide trading liquidity to buyers and sellers in exchange for a transaction fee. To join a pool, liquidity providers can send specific funds to a smart contract in exchange for pool tokens, earning passive profit based on the prices traders pay when they interact with that pool. Pool tokens are essential for recovering your deposited funds.

Yield farming is the process of maximizing returns through decentralized finance (DeFi). On a DeFi platform, users lend or borrow cryptocurrency in exchange for cryptocurrency. You can adopt various complicated strategies to boost your yield to optimize their gains, like shifting your cryptos between multiple loan platforms.
Yield farmers commonly use decentralized exchanges (DEXs) to lend, borrow, or stake coins to earn interest and speculate on price swings. Smart contracts, which are pieces of code that automate financial agreements between two or more parties, make yield farming possible across DeFi.
Types of Yield Farming
Let’s check out the different types of yield farming.
Lending and Borrowing
The whole idea behind DeFi lending is to offer crypto loans in a trustless manner without the need for any intermediaries. It also allows users to enlist their crypto coins on the platform for lending purposes. You can easily take a loan through a decentralized platform known as P2P lending. The lending protocol also allows the lender to earn interests.
Blockchain is the underlying technology for DeFi lending. Both Polkadot and Ethereum do a great job at that. Parallel Finance is an excellent example of a DeFi lending use case on Polkadot, while Compound Finance is a use case that runs on Ethereum.
The beautiful thing about DeFi is that it offers complete transparency with easier access to assets for every money transfer process without involving any third party.
The process of borrowing is very straightforward. You need to create an account on the DeFi platform and have a crypto wallet. DeFi provides a censorship-free environment, which means that no one gets special treatment while maintaining immutability.
Lending in DeFi benefits both lenders and borrowers because it offers margin trading options and allows long-term investors to lend assets and earn higher interest rates.
How Does DeFi Lending Work?
Most assets in a lending platform aren’t there just to generate interest. The real magic happens when we consider what lenders can accomplish. However, before we go into that, let us consider collateral.
You don’t need any permission to use a decentralized protocol; this makes traditional evaluations like credit score, equity, or income useless and can not be used to determine a safe loan amount. Instead, DeFi uses an over-collateralization technique, as I mentioned before. What happens is that the lending platform requires the borrowers to put up crypto assets as collateral.
Usually, these loans in DeFi are over-collateralized, which means that you can only receive a portion of what you put up for collateral as a borrower. If you lend $10,000 in Ether, you will acquire up to $7600 of DAI or other assets, giving approximately 75% of your collateral. This is just a measure to ensure that every user pays back their loan. If you can’t pay back what you borrowed, you will be at risk of liquidating your collateralized assets.
Liquidity Pools
Crypto is required for any economic activity to take place in DeFi. And that crypto needs to be supplied somehow, precisely the purpose of liquidity pools. A liquidity pool is a pool of tokens held in a smart contract, a self-executing program based on the agreements between the buyer and seller. Users can trade cryptocurrencies with the help of the pool, which provides liquidity. They are a necessary tool for many decentralized exchanges to facilitate their trading.

When a user sells token A to purchase token B on a decentralized exchange, they rely on tokens in the A/B liquidity pool provided by other users. When they are buying B tokens, there will be fewer B tokens in the pool, causing the price of B to rise. That’s essential supply and demand economics.
Popular Yield Farming Protocols
Curve Finance
Curve is the biggest DeFi platform in terms of total value locked, with nearly $19 billion on the platform. Because of its market-making algorithm, the Curve Finance platform uses locked funds more than any other DeFi platform. This is good for both swappers and liquidity providers.
Aave
In terms of stablecoin yield farming platforms, Aave is one of the most popular, with over $14 billion in locked-up value and over $3.4 billion. AAVE, the native token of Aave, is also available. Aave provides incentives such as fee reductions and governance voting power to encourage users to participate in the network’s services.
Uniswap
It is possible to exchange tokens without the need for trust using Uniswap, a DEX system. To create a market, liquidity providers invest two tokens. Traders can then trade against the liquidity pool. Liquidity providers receive fees from trades in their pool as a reward for their service.
Pancake Swap
PancakeSwap functions similarly to Uniswap; however, PancakeSwap operates on the Binance Smart Chain (BSC) network rather than the Ethereum network. It also has a few extra gamification-focused features. PancakeSwap offers BSC token exchanges, interest-earning staking pools, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and even a gambling game in which players predict the future price of Binance Coin (BNB).
Staking
Many long-term crypto holders see staking to make their assets work by generating rewards rather than just leaving their crypto dormant. Staking frequently necessitates a lockup period during which you cannot transfer your cryptocurrency.
Staking is a method of earning rewards for holding specific cryptocurrencies. This usually happens via a staking pool, which you can think of as being similar to an interest-bearing savings account. Your crypto earns rewards while staked because the blockchain puts it to work. Proof of Stake is a “consensus mechanism” used by cryptocurrencies that allow staking.
This is essentially a method of ensuring that all transactions are verified and secure without the involvement of a bank or payment processor. If you choose to stake your cryptocurrency, it becomes a part of that process.
Staking helps the security and efficiency of the blockchain projects you support. Taking some of your funds makes the blockchain more resistant to attacks and improves its ability to process transactions.
Anyone who wants to participate in staking can do so. To become a full validator, you need a significant minimum investment, technical knowledge, and a dedicated computer. This computer should be capable of performing validations at any time of day or night without downtime. Participating at this level has security implications and is a serious commitment, as downtime can reduce a validator’s stake.
However, there is an easier way for some of us to participate via centralized exchanges, like Binance or Coinbase. You can contribute any amount you want to a staking pool here. This lowers the entry barrier and allows investors to begin earning rewards without operating their own validator hardware.
Stablecoins and Payments
Stable capital is a requirement for DeFi to be categorized as a financial system with the ability to perform transactions and enter into contracts. Participants must trust that their assets will not lose value like other cryptocurrencies. This is where stablecoins come in. Stablecoins stabilize the typical lending and borrowing activities in the DeFi market. Stablecoins, which use a fiat currency like the U.S. dollar or the euro, are less volatile than cryptocurrencies and thus more suitable for trading and commerce.

Solving the Scalability Issue of DeFi
For DeFi to be scalable, the blockchain that powers it must also be scalable. I’ve used some platforms, and their transactions are painfully slow. This will remain an issue until developers resolve the scalability issue. This issue prompted the creation of Ethereum 2.0. Recently, I’ve seen new and exciting DeFi projects emerge, such as Parallel Finance. Parallel Finance is a decentralized money market protocol in the Polkadot ecosystem that allows for lending, staking, and borrowing.

Depositors can lend and stake simultaneously to earn a double yield on their staked coins, and borrowers can borrow using collateral.
I believe this project has a lot of potential to solve the scalability problem because it uses the Polkadot network, which is scalable and allows for the execution of many transactions on multiple chains in parallel. This eliminates bottlenecks on chains that process transactions one at a time and vastly improves scalability.
The First Use Case of DeFi are Decentralized Exchanges
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) take a different approach to buying and selling digital assets. They operate without an intermediary organization for clearing transactions, relying instead on self-executing smart contracts to facilitate trading. When you trade on a DEX, there’s no exchange operator, no signups, no identity verification, and no withdrawal fees. Instead, the smart contracts enforce the rules, execute trades and securely handle funds. Unlike a centralized exchange, there is no need to deposit funds into an exchange account before conducting a transaction. This eliminates the significant risk of exchange hacking for all centralized exchanges. Some of the major centralized exchanges are
- Binance
- Bittrex
- Bitfinex
- Coinbase
- Kraken
Some of the Major Decentralised Exchange are:
- Uniswap
- PancakeSwap
- dYdX
- ApolloX DEX
- TraderJoe
- Sushiswap
Wallets and Aggregators
Aggregators are simply the interfaces through which users interact with the DeFi market. They are, in essence, decentralized asset management platforms that automatically move users’ crypto assets between various yield-farming platforms to maximize returns. Wallets are storage hubs for digital assets that can store multiple or just one. They come in multiple forms, including software, hardware, and exchange wallets.

Now that we know about stable coins, decentralized exchanges, and decentralized money markets, how about decentralized insurance? A decentralized platform connects people willing to pay for insurance with people eager to insure them for a premium.
DeFi services work in conjunction with one another, making it possible to mix and match different services to create new and exciting opportunities.
Let’s liken this scenario to LEGO blocks. The term money legos has been coined to refer to DeFi services. You can use these Lego blocks for borrowing, staking, or lending assets, and they put them together to create a single multi-functional financial application.
Once the developer has selected the number of Legos needed to create their project, they can be pushed together, like Lego blocks, to create a new protocol. This protocol will be built on the blockchain and run by a smart contract.
For instance, you can start by using a decentralized exchange aggregator like DEX.Ag to find the exchange with the best rate for swapping Ether for Dai. Then select the DEX (i.e., Uniswap) you want and conduct the trade of Ether for Dai. Then you lend the DAI you received via AAVE to borrowers to earn interest. Finally, you can add insurance to this process to ensure you are covered if anything goes wrong.
DeFi Presents Numerous Advantages
- Permissionless” to create, “permissionless” to participate — anyone can create and use DeFi applications without permission. In contrast to modern finance, there are no gatekeepers or lengthy account forms. Users interact with smart contracts directly through their cryptocurrency wallets.
- Transparency Anyone can audit the code on the blockchain. This builds user trust because anyone can understand the contract’s functionality or find bugs. Anyone can view all transaction activity. While this may raise privacy concerns, all transactions are pseudonymous by default.
- Flexible user experience — If you don’t like the U.I. of a particular dapp? You can use a third-party interface or create your own. Smart contracts are similar to an open API for which anyone can create an app.
- Interoperability – Stablecoins, decentralized exchanges, and prediction markets, for example, can be combined to form entirely new DeFi applications by combining other DeFi products like Lego pieces.
- DApps are global from the start, so whether you’re in Nigeria or the United Kingdom, you can use the same DeFi services and networks. Although some restrictions may apply, most DeFi apps are technically available to anyone with an internet connection.
Summary
DeFi is still in its infancy, which means that things can go wrong. Smart contracts have had issues where people didn’t define the rules for specific services accurately, and hackers found creative ways to exploit loopholes to steal money.
A website you should have on your radar is defipulse.com.


Great article! Helped me understand Defi better.
Thanks chief. I’m glad it helped
Nice article, quite in-depth.
I enjoyed reading it.
I’ll be looking forward to more articles like this from decentrapress
Thanks Akorede, will sure not disappoint you
🙌🙌🙌🙌🙌 well written
Thanks Dr Chigbo
Detailed and easy to understand. It’s a really nice one👍🏻
Thanks alot Titilope
Amazing….
This article is impressive and carefully written
Thanks alot stephanie
Nice article very easy to understand
Looking forward to read more from you
Thannks Toyoflow
Incisive and brilliant..
Keep the flag flying.
Thanks mastermind
Interesting. I have been wondering about all these new technologies and financial systems. This articles lays a foundation for newbies and its quite easy to follow and understand. Thanks for sharing
Thanks alot Mofolusade
This article is very detailed and easy to grasp. I’m hoping to see more of other blockchain topics covered on this blog.
Thanks Dharmelolar
[…] web or what we now know today as Web3. In my last article, I explained in dept what DeFi (decentralized finance is all about) Today we are going to be going in-depth about DAO. I kinda love the acronyms used in Web3, they […]
I love this piece, you broke it down in such a way that someone who is not knowledgeable about crypto would understand. Well done !!!
Thanks alot Tobi
[…] is the holy grail of decentralization. I have written about DAO and DeFI extensively. Without Ethereum non of those can exist. Ethereum is the community-run technology […]
Thanks alot
[…] wallet lets you connect to any decentralized application using your Ethereum account. It’s like a login you can use across many […]
[…] DEX did not get as much attention as expected when it was created due to the accomplishments of Defi on Ethereum. Smart contracts were not a part of the Binance Chain during its creation and that was fast […]
[…] Samuel also went into great detail about the meaning and concept of DeFi. You can read more about it in this article. […]
[…] hand, are highly volatile in terms of market value, which is constantly changing. If you read my DeFi article, you’ll know that if you want to build a DeFi application, you’ll need a stable, not […]